Imagine your website as a massive library – each page on your website represents a book full of valuable information, waiting to be explored by visitors (search engines and readers).
Now put yourself in your visitor’s shoes. Without a proper indexing system, they can never find their way from one book to the next. In fact, they might never even be able to find the one book they were looking for in the first place!
That’s where internal linking comes in.
Internal linking, although highly underrated, is a crucial aspect of SEO that you should optimize. It significantly determines whether your pages get crawled and indexed by search engines, and whether your readers can fully explore and enjoy your website.
But we all know how tricky internal linking can be – it is time-consuming and often confusing. However, it doesn’t have to be that way, especially if you know the right way to do it and what tools to use.
In this post, you will learn what internal linking is, why it’s important, and how to do it – the right way.
What Are Internal Links?
Internal links are hyperlinks that point from one page to another within the same domain. They’re like the connective tissue of your website, guiding users and search engines through all your pages and posts.
For website visitors, internal links enhance user experience by providing further reading options or directing them to important information. For instance, a blog post about “The Best Running Shoes” might include internal links to related articles like “How to Choose Running Shoes” or product pages for recommended shoes. It keeps users engaged and encourages them to explore more of your site.
For search engines, internal links help them discover new pages on your site, which speeds up the crawling and indexing process. If search engines don’t know your page exist, this page in question will never have a chance of appearing on search results, let alone rank and bring you traffic.
But more on the importance of internal linking later.
Types of Internal Links
Now that you know what internal links are, you should also know that not all internal links are one and the same.
There are three types of internal links:
1. Contextual Internal Links
Contextual internal links are links within the body of a content, linking relevant texts within articles to other pages on the site. They provide easy access to additional information by connecting readers to related content within a website.
Contextual links typically use anchor text that is colored differently than the surrounding text. This distinct visual cue helps readers identify the linked text and encourages them to navigate to other relevant pages on the website.
For example, a blog post about healthy eating might have certain phrases that link to related recipes or nutritional guides. These are contextual links.
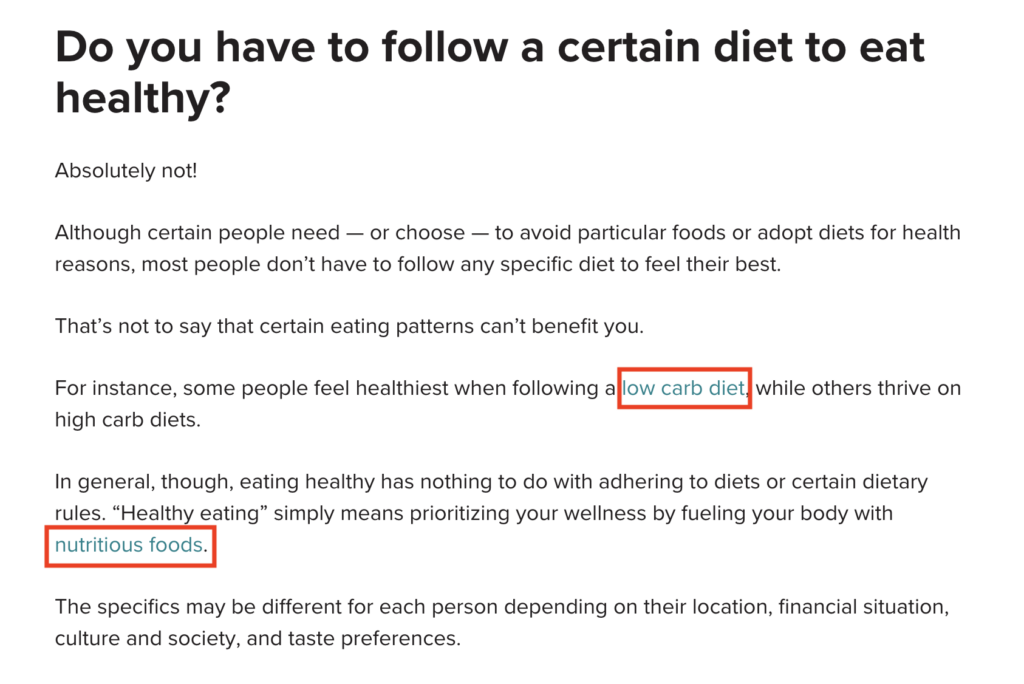
2. Navigational Internal Links
Navigational internal links are like the signposts on a website, guiding visitors to major sections or pages. They’re often found in menus, including the header or sidebar.
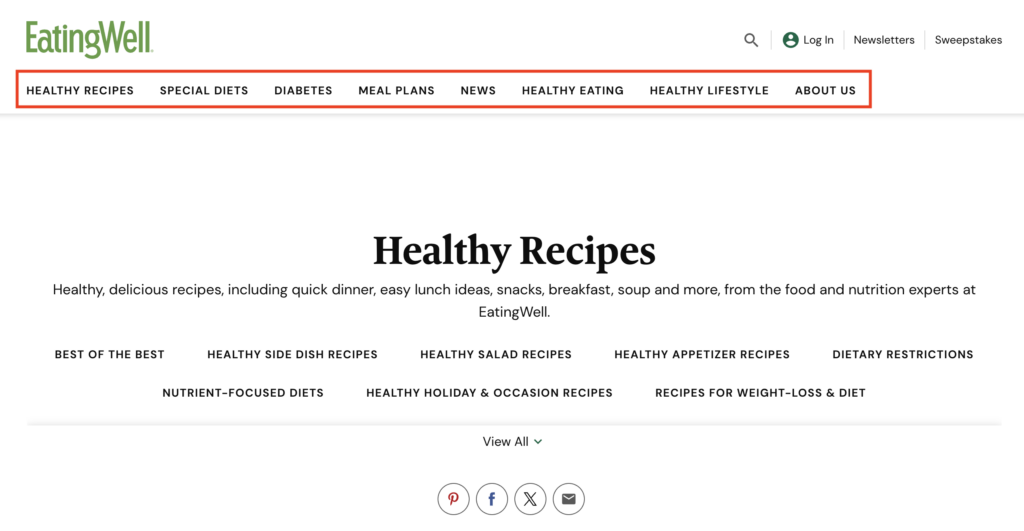
Most websites include their key pages on their header menu so users can easily access those pages. Some typical pages you’ll see are:
- Blog & Blog Categories
- Product Categories
- About Us
- Pricing
The header will also always include the homepage link so users can easily go back to the main page no matter where they are currently on the website.
3. Footer Internal Links
Footer internal links sit at the bottom of every page and typically include links to privacy policies, terms of use, sitemaps, and contact pages.
Similar to the navigational links, footer links act as a safety net for navigation, ensuring users can find essential information regardless of where they are on your site.

Why Are Internal Links Important?
So, why should you care about internal linking? How do they benefit you?
Here are 3 reasons why internal links are important:
1. Improves Your Rankings & Traffic
Internal links do wonders for your site’s search engine optimization (SEO). They help search engines discover new pages on your site, allowing them to navigate and index your content more effectively. This ensures all your pages get indexed faster and show up on search results.
Also, by linking related content, you signal to search engines that there’s more valuable information on your site. It shows that your site has depth and value in a specific subject area. This builds up your topical authority, which leads to better rankings in search results.
2. Enhances User Experience
Additionally, internal links make your website easier to navigate. They guide visitors through your site, leading them from one piece of content to another. This not only keeps people on your site longer (reducing bounce rates!) but also makes it more likely they’ll find the information they need.
What this also means is that it significantly increase page views on your website. When readers find links to topics they’re interested in, they’re more likely to click through and continue reading.
This reduction in bounce rates and positive user experience signal to search engines that your site is engaging and valuable. More page views also mean increased opportunities for conversions, whether that’s signing up for a newsletter or making a purchase.
3. Distributes Page Authority
Internal links also pass authority or “link juice” from one page to another within your website.
Because pages with higher authority rank better in search results, distributing this authority throughout your site can boost the performance of individual pages.
This means high-performing pages can share their success with less visible pages by linking to them. It’s a way of lifting all boats with the tide of a few successful pieces.
Best Practices & Mistakes to Avoid in Internal Linking
To get the most benefits out of internal linking, you need to make sure you’re doing it right.
When done right, search engines and readers will love your website and consequently, you will rank higher and get more traffic. Conversely, if you do it wrong, it will ruin all your hardwork and mess up your website.
Here are best practices to follow when doing internal linking:
1. Use Relevant Anchor Text
Make sure to use descriptive and relevant anchor text that accurately reflect the content they are linking to.
To do this, you can use keywords that summarize the linked content and provide context for the reader. For example, instead of using generic phrases like “click here” or “read more,” opt for specific anchor text like “learn more about SEO strategies” or “tips for improving website traffic.”
Also, make sure that the anchor text blends in well with the surrounding text. Don’t force an anchor text in where it doesn’t fit to the point that it reads unnatural and disrupts the user experience. Avoid using overly long or convoluted anchor text that may confuse readers or dilute the relevance of the link.
Additionally, try to maintain a healthy balance of anchor text variation for the same link. This means using both exact match keywords and partial match keywords.
An example of exact match anchor text could be “best hiking boots for women,” where the anchor text exactly matches the keyword phrase. On the other hand, a partial match anchor text example could be “top-rated women hiking boots,” which includes some of the keywords and essentially mean the same thing.
You want to avoid repetitive anchor text throughout your website, as this hinders the user experience and impact your site’s SEO performance. Repetitive anchor text are unnatural, which sends the wrong signals to search engines.
2. Link to Relevant Pages
When doing internal linking, consider the context and relevance of the content you are linking to. Make sure that pages being linked are relevant, and avoid linking just for the sake of linking.
A helpful way to do this is by considering the user journey. When reading a specific article, what would your reader want to know next or need more information about? This helps you pinpoint which pages to link to.

3. Avoid Overlinking
Moderation is key in internal linking – don’t go overboard with too many internal links on a single page. Overlinking can distract readers and make your content feel spammy. Instead, focus on including links that truly enhance the reader’s experience by providing additional valuable information or resources.
Placement also matters. Avoid placing too many links too close in proximity to each other. This can overwhelm readers and make your content appear cluttered. Instead, strategically space out your links throughout the text to ensure they are easily accessible and not disruptive to the reader’s flow.

4. Create a Hierarchical Structure
Building a hierarchical structure of all your content can help immensely in organizing your internal links.
By organizing your links in a hierarchical manner, you make it easier for visitors to find important pages and information on your site. This also helps search engines understand the structure of your website better.
To create a hierarchical structure, start by identifying the most important pages on your site. These could be your homepage, category page, or pillar page (a page that covers a broad topic). Then, link these important pages from multiple places on your site, such as the navigation menu, footer, sidebar, and within relevant content.
Avoid creating too many levels of hierarchy, as this can confuse users and make it harder for them to navigate your site.
For example, if you have an e-commerce website, you could have a top-level category for “Products,” with subcategories for different product types (e.g., clothing, electronics, accessories). Within each subcategory, link to specific product pages to guide users through the buying process.
5. Fix Broken Links
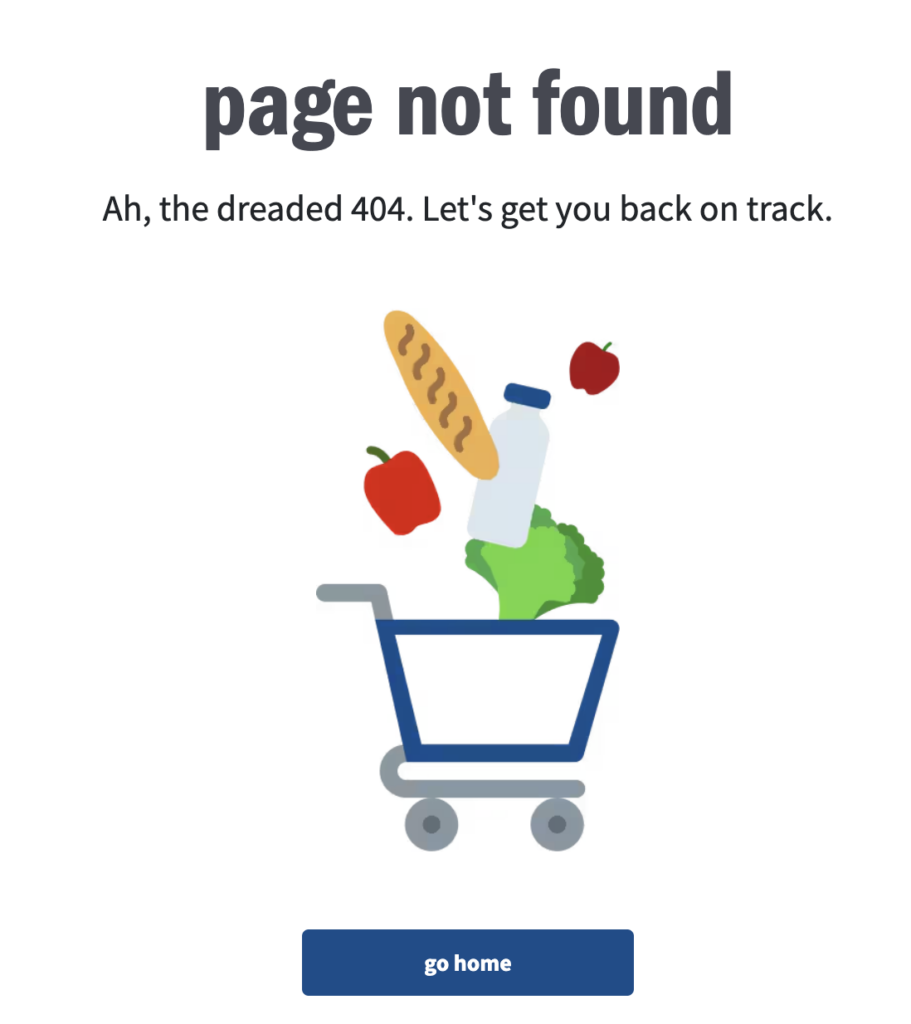
Broken links are links that point to a page that doesn’t exist, often leading to error pages such as a 404 error. Having broken links on a website can lead to a frustrating user experience and negatively impact your site’s credibility and SEO performance.
For example, if a user clicks on a broken internal link on your website and ends up on an error page, they may become frustrated and leave your site altogether. This can result in a high bounce rate and lower user engagement. Additionally, search engines like Google may penalize your site for having too many broken links, affecting your SEO rankings.
Hence, it’s crucial to regularly check for broken internal links and resolve them. One specific way to do this is by using tools like LinkVector which tells you whether you have broken links. It will scan your website and provide a list of broken links that need to be fixed. Once you have identified broken links, you can promptly fix them by updating the URLs or removing the links altogether.
6. Utilize Breadcrumbs
Do you ever get lost in a website with hundreds of pages because you went down the rabbit hole of a really interesting topic, and couldn’t find your way back? This is where breadcrumbs come in.
Breadcrumbs are a mighty helpful navigation tool that can guide users back to where they started on a website. They provide a trail of links that show the user the path they took to get to their current location (just like breadcrumbs!). This can be especially useful for websites with a lot of content or pages, as it can be easy to get lost in the vast amount of information available.
By using breadcrumbs, users can easily retrace their steps and find their way back to the main page or section they were originally exploring. This improves the overall user experience and make navigating a website much more intuitive and user-friendly.
7. Link from High-Authority Pages
Every website has some pages that rank higher in search results and attract more visitors than others. These are your high-authority pages. You can leverage their strength to help your lower-authority pages perform better through strategic internal linking.
Here’s how it works: When you include a link to a lower-authority page from a high-authority page on your website, you’re essentially passing on some of that page’s “link juice” or ranking power. Search engines view these links as a vote of confidence, and it can give your lower-authority page a boost in search engine results.
8. Make Sure Important Pages are Within 3 Clicks Away From the Homepage
It is really, really, really important to ensure your key pages are accessible within just a few clicks from the homepage (three clicks or less!). This practice not only helps visitors easily access important pages but also signals to search engines the significance of these pages.
This also improves the chances of these pages getting indexed and ranked higher in search results, ultimately driving more organic traffic to your website.
9. Update Old Content
As you publish new content, new opportunities for internal linking will arise, both from the new content to old content, and from the old content to the new one. While most people practice linking from new content to old, most overlook doing it vice versa, ie. from old content to new.
Why? Because it’s a hassle to sift through older content, identify the linking opportunities, and actually inserting them. Imagine a website with hundreds of existing content – this will take days, even months to do.
However, doing this is extremely crucial. When you publish new content, search engines won’t instantly know it exists. Without any known source linking to it, search engines might take a while to discover, crawl, and index your new page.
When you link from an older content that search engines know of, you’ll direct search engines to crawl the new page you just published. This greatly speeds up the crawling process and effectively get you ranked faster.
How to Do Internal Linking
Great, now you’re a pro in internal linking. You know why it’s important, what to do, and what not to do. Time to roll up your sleeves and actually get into it.
But how do you do it? Where do you even start?
There are two main methods to tackle internal linking: the hard way or the easy way.
Let’s break down both.
1. Manual Internal Linking (The Hard Way)
The manual approach involves individually selecting pages and deciding where links should go.
This method requires you to comb through your content, identify relevant keywords, and link them to corresponding pages within your site.
It sounds straightforward but can be incredibly time-consuming and inefficient, especially for larger sites with hundreds or thousands of pages.
One major drawback is the risk of missing opportunities for optimal linking due to human error.
As your website grows and evolves, keeping track of all these links and their relevance becomes a Herculean task.
This method might provide more control over each link’s placement and relevance but at the cost of scalability and efficiency.
2. Use Internal Linking Tools to Automate (The Easy Way)
For a more efficient way of doing internal linking, using an automated internal linking tool is highly recommended.
However, you’d have to be extra vigilant when using tools. Most internal linking tools rely on overly-simple rules that only look at keywords and fail to consider context. This often results in irrelevant pages being linked together, unnatural and low-quality anchor text, and a fractured site structure. You have to thoroughly review the suggestions presented to you and not trust them 100% – which, let’s face it, is a huge waste of time.
This is where LinkVector comes in. Different from other existing tools, LinkVector employs highly-sophisticated technology that considers context and relevance when doing internal linking.
LinkVector scans your entire website, analyzes your content, and finds natural linking opportunities based on relevancy and keyword optimization. It then automatically creates these links across your site, saving you considerable time and effort.
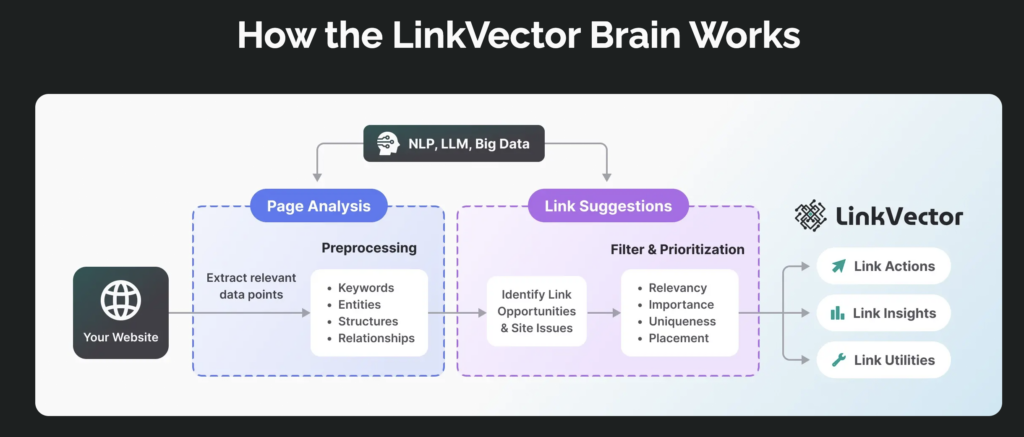
Using an automated internal linking tool like LinkVector ensures that no potential link is overlooked and maintains an up-to-date internal linking structure even as new content is added. This ensures a solid link architecture that improves user navigation and helps search engines crawl your site more effectively.
The best thing about LinkVector is that it adheres closely to internal linking best practices to ensure your internal linking strategy is of the highest quality.
Going a step above other internal linking tools, LinkVector also comes with a few perks you won’t find elsewhere:
- Relevant links with natural placements, avoiding nonsensical and irrelevant links.
- Descriptive and context-matching anchor texts, optimized for both users and SEO.
- Automated insertion of internal links, saving time and effort.
- Bulk internal linking actions, eliminating the need for manual linking.
- Compatibility with any website and any CMS, not just limited to WordPress.
- A visual representation of internal links, helping you clearly see how your pages are connected.
- Helps you diagnose and fix 18 page and link issues based on Google guidelines.
Interlink Your Website Now
Internal linking is not just about throwing links here and there; it’s about creating a smart web that guides users and search engines through your site like a well-organized library.
While internal linking can be done manually or through internal linking tools for convenience, your best bet to get high-quality, precise, and fast internal linking is none other than with LinkVector.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are internal links?
Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page of a website to another page within the same website. They help users navigate and find content easily.
Why are internal links important for SEO?
Internal links spread link equity (value) throughout your site, which can boost the ranking power of your pages in search engine results. They also improve site navigation, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site.
What types of internal links exist?
There are mainly two types: navigational links, found in menus and sidebars, and contextual links, which are embedded in articles and connect readers to related content.
How do internal and external links differ?
Internal links connect pages within the same website, while external links point from your site to different domains. Both are crucial for SEO but serve different purposes like improving site structure or establishing authority.
Can too many internal links hurt my SEO?
Yes, overloading a page with irrelevant internal links can dilute link value and confuse both users and search engines about the most important pages, potentially harming your SEO efforts.
Is there an ideal number of internal links per page?
No fixed number works best for all websites, but it’s wise to use them as naturally as possible within the content. Ensure each link adds value for the reader and helps search engines understand your site’s structure.
